Abstract Fibonaccii Hack
A Fibonacci algorithm that runs using an abstract parent class.
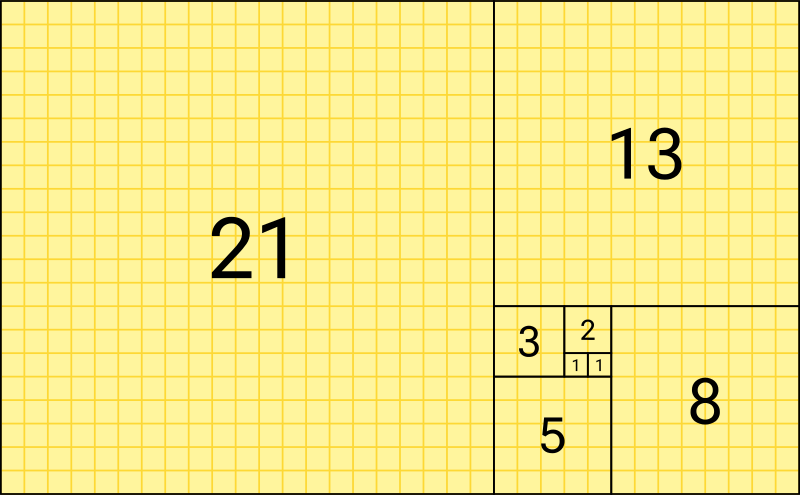
Introduction
This notebook uses Class definitions, ArrayLists, and Hash Maps. My hypothosis is these data structures are probably the most widely used in the Java language.
Popcorn Hacks
- Provide some reasons why you agree with my hypothesis?
These might be the most used as encapsulation and OOP are these are class definitions, as they usually come with a constructor, a fundamental block of OOP.
ArrayLists are easy to use for it’s resizability. Hashmaps offer speed with O(1) time complexity for getting values from a key, and these classes are quite literally on the AP exam.
- Provide some data structures that you think might rival my hypothesis?
Structures such as HashSets, LinkedLists, and what notebooks are typically used for being testing experimental features such as using matplotlib for Python based notebooks, may lead to less usage of these structures.
- Categorize data structure mentioned, tested by college board tested, widely used, fast.
| Data Structure | Tested by CollegeBoard | Widely Used | Fast |
|---|---|---|---|
| Class Definition | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| ArrayList | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| HashMap | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Hashset | No | Yes | Yes |
| LinkedList | No | Yes | Slower |
/*
* Creator: Nighthawk Coding Society
* Mini Lab Name: Fibonacci sequence, featuring a Stream Algorithm
*
*/
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
/* Objective will require changing to abstract class with one or more abstract methods below */
abstract class Fibo {
String name; // name or title of method
int size; // nth sequence
int hashID; // counter for hashIDs in hash map
ArrayList<Long> list; // captures current Fibonacci sequence
HashMap<Integer, Object> hash; // captures each sequence leading to final result
/*
Zero parameter constructor uses Telescoping technique to allow setting of the required value nth
@param: none
*/
public Fibo() {
this(8); // telescope to avoid code duplication, using default as 20
}
/*
Construct the nth fibonacci number
@param: nth number, the value is constrained to 92 because of overflow in a long
*/
public Fibo(int nth) {
this.size = nth;
this.list = new ArrayList<>();
this.hashID = 0;
this.hash = new HashMap<>();
//calculate fibonacci and time mvc
this.calc();
}
/*
This Method should be "abstract"
Leave method as protected, as it is only authorized to extender of the class
Make new class that extends and defines calc()
Inside references within this class would change from this to super
Repeat process using for, while, recursion
*/
protected abstract void calc();
/*
Number is added to fibonacci sequence, current state of "list" is added to hash for hashID "num"
*/
public void setData(long num) {
list.add(num);
hash.put(this.hashID++, list.clone());
}
/*
Custom Getter to return last element in fibonacci sequence
*/
public long getNth() {
return list.get(this.size - 1);
}
/*
Custom Getter to return last fibonacci sequence in HashMap
*/
public Object getNthSeq(int i) {
return hash.get(i);
}
/*
Console/Terminal supported print method
*/
public void print() {
System.out.println("Calculation method = " + this.name);
System.out.println("fibonacci Number " + this.size + " = " + this.getNth());
System.out.println("fibonacci List = " + this.list);
System.out.println("fibonacci Hashmap = " + this.hash);
for (int i=0 ; i<this.size; i++ ) {
System.out.println("fibonacci Sequence " + (i+1) + " = " + this.getNthSeq(i));
}
}
}
public class FiboFor extends Fibo {
public FiboFor() {
super();
}
public FiboFor(int nth) {
super(nth);
}
@Override
protected void calc() {
super.name = "FiboFor extends Fibo";
long limit = this.size;
// for loops are likely the most common iteration structure, all the looping facts are in one line
for (long[] f = new long[]{0, 1}; limit-- > 0; f = new long[]{f[1], f[0] + f[1]})
this.setData(f[0]);
}
/*
Tester class method.
*/
static public void main(int... numbers) {
for (int nth : numbers) {
Fibo fib = new FiboFor(nth);
fib.print();
System.out.println();
}
}
}
FiboFor.main(2, 5, 8);
Calculation method = FiboFor extends Fibo
fibonacci Number 2 = 1
fibonacci List = [0, 1]
fibonacci Hashmap = {0=[0], 1=[0, 1]}
fibonacci Sequence 1 = [0]
fibonacci Sequence 2 = [0, 1]
Calculation method = FiboFor extends Fibo
fibonacci Number 5 = 3
fibonacci List = [0, 1, 1, 2, 3]
fibonacci Hashmap = {0=[0], 1=[0, 1], 2=[0, 1, 1], 3=[0, 1, 1, 2], 4=[0, 1, 1, 2, 3]}
fibonacci Sequence 1 = [0]
fibonacci Sequence 2 = [0, 1]
fibonacci Sequence 3 = [0, 1, 1]
fibonacci Sequence 4 = [0, 1, 1, 2]
fibonacci Sequence 5 = [0, 1, 1, 2, 3]
Calculation method = FiboFor extends Fibo
fibonacci Number 8 = 13
fibonacci List = [0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13]
fibonacci Hashmap = {0=[0], 1=[0, 1], 2=[0, 1, 1], 3=[0, 1, 1, 2], 4=[0, 1, 1, 2, 3], 5=[0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5], 6=[0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8], 7=[0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13]}
fibonacci Sequence 1 = [0]
fibonacci Sequence 2 = [0, 1]
fibonacci Sequence 3 = [0, 1, 1]
fibonacci Sequence 4 = [0, 1, 1, 2]
fibonacci Sequence 5 = [0, 1, 1, 2, 3]
fibonacci Sequence 6 = [0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5]
fibonacci Sequence 7 = [0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8]
fibonacci Sequence 8 = [0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13]
public class FiboStream extends Fibo {
public FiboStream() {
super();
}
public FiboStream(int nth) {
super(nth);
}
@Override
protected void calc() {
super.name = "FiboStream extends Extends";
// Initial element of stream: new long[]{0, 1}
// Lambda expression calculate the next fibo based on the current: f -> new long[]{f[1], f[0] + f[1]}
Stream.iterate(new long[]{0, 1}, f -> new long[]{f[1], f[0] + f[1]})
.limit(super.size) // stream limit
.forEach(f -> super.setData(f[0]) ); // set data in super class
}
/*
Tester class method.
*/
static public void main(int... numbers) {
for (int nth : numbers) {
Fibo fib = new FiboFor(nth);
fib.print();
System.out.println();
}
}
}
FiboStream.main(2, 5, 8);
Calculation method = FiboFor extends Fibo
fibonacci Number 2 = 1
fibonacci List = [0, 1]
fibonacci Hashmap = {0=[0], 1=[0, 1]}
fibonacci Sequence 1 = [0]
fibonacci Sequence 2 = [0, 1]
Calculation method = FiboFor extends Fibo
fibonacci Number 5 = 3
fibonacci List = [0, 1, 1, 2, 3]
fibonacci Hashmap = {0=[0], 1=[0, 1], 2=[0, 1, 1], 3=[0, 1, 1, 2], 4=[0, 1, 1, 2, 3]}
fibonacci Sequence 1 = [0]
fibonacci Sequence 2 = [0, 1]
fibonacci Sequence 3 = [0, 1, 1]
fibonacci Sequence 4 = [0, 1, 1, 2]
fibonacci Sequence 5 = [0, 1, 1, 2, 3]
Calculation method = FiboFor extends Fibo
fibonacci Number 8 = 13
fibonacci List = [0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13]
fibonacci Hashmap = {0=[0], 1=[0, 1], 2=[0, 1, 1], 3=[0, 1, 1, 2], 4=[0, 1, 1, 2, 3], 5=[0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5], 6=[0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8], 7=[0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13]}
fibonacci Sequence 1 = [0]
fibonacci Sequence 2 = [0, 1]
fibonacci Sequence 3 = [0, 1, 1]
fibonacci Sequence 4 = [0, 1, 1, 2]
fibonacci Sequence 5 = [0, 1, 1, 2, 3]
fibonacci Sequence 6 = [0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5]
fibonacci Sequence 7 = [0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8]
fibonacci Sequence 8 = [0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13]
Popcorn Hacks
Objectives of these hacks are …
-
Understand how to fullfill abstract class requirements using two additional algoritms.
- Use inheritance style of programming to test speed of each algorithm. To test the speed, a.) be aware that the first run is always the slowest b.) to time something, my recommendation is 12 runs on the timed element, through out highest and lowest time in calculations.
- Be sure to make a tester and reporting methods.
.85 basis for text based comparison inside of Jupyter Notebook lesson
Hacks
Assign in each Team to build a Thymeleaf UI for portfolio_2025 using this example https://thymeleaf.nighthawkcodingsociety.com/mvc/fibonacci as basis. Encorporate into Algorithms menu.
Since there are three teams, one team can do Fibo, others Pali and Factorial. Assign this to people that are struggling for contribution and presentation to checkpoints.
.90 basis for FE presentation in Thymmeleaf to BE call in Spring
public class FibonacciRecursive extends Fibo {
public FibonacciRecursive(int n) {
super(n);
this.name = "Recursive Fibonacci";
}
@Override
protected void calc() {
for (int i = 0; i < this.size; i++) {
setData(fib(i));
}
}
/**
* Recursive Fibonacci function
*/
private long fib(int n) {
if (n <= 1) return n; // Base cases: F(0) = 0, F(1) = 1
return fib(n - 1) + fib(n - 2);
}
}
FibonacciRecursive fibo = new FibonacciRecursive(11);
fibo.print();
Calculation method = Recursive Fibonacci
fibonacci Number 11 = 55
fibonacci List = [0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55]
fibonacci Hashmap = {0=[0], 1=[0, 1], 2=[0, 1, 1], 3=[0, 1, 1, 2], 4=[0, 1, 1, 2, 3], 5=[0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5], 6=[0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8], 7=[0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13], 8=[0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21], 9=[0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34], 10=[0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55]}
fibonacci Sequence 1 = [0]
fibonacci Sequence 2 = [0, 1]
fibonacci Sequence 3 = [0, 1, 1]
fibonacci Sequence 4 = [0, 1, 1, 2]
fibonacci Sequence 5 = [0, 1, 1, 2, 3]
fibonacci Sequence 6 = [0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5]
fibonacci Sequence 7 = [0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8]
fibonacci Sequence 8 = [0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13]
fibonacci Sequence 9 = [0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21]
fibonacci Sequence 10 = [0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34]
fibonacci Sequence 11 = [0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55]
public class FibonacciMatrix extends Fibo {
public FibonacciMatrix(int n) {
super(n);
this.name = "Matrix Exponentiation";
}
@Override
protected void calc() {
for (int i = 0; i < this.size; i++) {
setData(matrixToAPower(i));
}
}
/**
* Multiply two 2x2 matrices.
*/
private int[][] multiplyMatrix(int[][] a, int[][] b) {
int[][] mat = new int[2][2];
mat[0][0] = a[0][0] * b[0][0] + a[0][1] * b[1][0];
mat[0][1] = a[0][0] * b[0][1] + a[0][1] * b[1][1];
mat[1][0] = a[1][0] * b[0][0] + a[1][1] * b[1][0];
mat[1][1] = a[1][0] * b[0][1] + a[1][1] * b[1][1];
return mat;
}
/**
* Raise a 2x2 matrix to the power of n.
*/
private int matrixToAPower(int n) {
if (n == 0) return 0; // F(0) = 0
if (n == 1) return 1; // F(1) = 1
int[][] result = { {1, 0}, {0, 1} }; // Identity matrix
int[][] base = { {1, 1}, {1, 0} }; // Fibonacci special matrix
while (n > 0) {
if (n % 2 == 1)
result = multiplyMatrix(result, base);
base = multiplyMatrix(base, base);
n /= 2;
}
return result[0][1];
}
}
FibonacciMatrix fibo = new FibonacciMatrix(11);
fibo.print(); // Print results
Calculation method = Matrix Exponentiation
fibonacci Number 11 = 55
fibonacci List = [0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55]
fibonacci Hashmap = {0=[0], 1=[0, 1], 2=[0, 1, 1], 3=[0, 1, 1, 2], 4=[0, 1, 1, 2, 3], 5=[0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5], 6=[0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8], 7=[0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13], 8=[0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21], 9=[0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34], 10=[0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55]}
fibonacci Sequence 1 = [0]
fibonacci Sequence 2 = [0, 1]
fibonacci Sequence 3 = [0, 1, 1]
fibonacci Sequence 4 = [0, 1, 1, 2]
fibonacci Sequence 5 = [0, 1, 1, 2, 3]
fibonacci Sequence 6 = [0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5]
fibonacci Sequence 7 = [0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8]
fibonacci Sequence 8 = [0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13]
fibonacci Sequence 9 = [0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21]
fibonacci Sequence 10 = [0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34]
fibonacci Sequence 11 = [0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55]
//test reporter
public static void testSpeed(Fibo fiboInstance) {
int runs = 12;
ArrayList<Long> times = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < runs; i++) {
long start = System.nanoTime();
fiboInstance.calc();
long end = System.nanoTime();
times.add(end - start);
}
// Remove highest and lowest times for more accuracy
times.remove(Collections.max(times));
times.remove(Collections.min(times));
long avgTime = times.stream().mapToLong(Long::longValue).sum() / times.size();
// Print results
System.out.println("Solver: " + fiboInstance.name);
System.out.println("Size " + fiboInstance.size + " " + fiboInstance.getNth());
System.out.println("Average Time: " + avgTime / 1e6 + " ms");
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------");
}
int n = 20;
testSpeed(new FibonacciRecursive(n));
testSpeed(new FiboFor(n));
testSpeed(new FibonacciMatrix(n));
Solver: Recursive Fibonacci
Size 20 4181
Average Time: 0.254833 ms
-----------------------------------------
Solver: FiboFor extends Fibo
Size 20 4181
Average Time: 0.010024 ms
-----------------------------------------
Solver: Matrix Exponentiation
Size 20 4181
Average Time: 0.116514 ms
-----------------------------------------