Unit 8 - 2D Arrays Intro - P1
2D Arrays Lesson
Learning Objectives
The objective of this lesson is to…
- Learn about 2D arrays, their use cases, and how to create them.
Essential Knowledge
College Board wants you to know…
- How to declare/initialize 2D arrays.
- How to determine their size.
- How to access and update the values of a 2D array.
- How to traverse/access elements of a 2D array using nested iteration statements.
- How nested iteration statements can be used to traverse 2D arrays in “row-major order” vs “column-major order.”
- How to create algorithms that require the use of 2D array traversals.
Warm Up
Answer the following questions as a group or individually. Write down your answers in your hacks notebook.
- What are 2D arrays?
2D Arrays are arrays with an extra dimension. They are data structures in Java.
- How are 2D arrays organized?
2D arrays are organized into rows and columns in a matrix format. There are two indices, one for rows and one for columns.
- What are some real-world examples of 2D arrays?
Some real-world examples of 2D arrays can be spreadsheets or maybe image processing.
The Basics/Recap
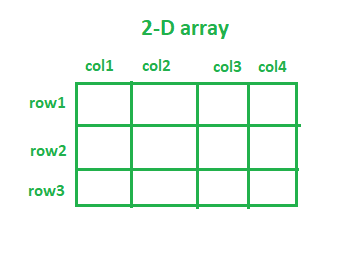
2D arrays, and higher dimension arrays overall, can be thought of as just an array that’s made up of other arrays or an array of arrays. One way of looking at 2D arrays is by thinking of them as a chess board. They have rows and columns, and every element is identified via row or column number or index.
Below is an illustration of a 2D array:
Warmup (Review)
- For the following three code cells categorize data + organization
- Data Bank: Homogenous Data, Heterogeneous Data, Type of Data, Heterogeneous Dimensions, Non-Square
- Note: Datatypes can be reused