Unit 5 Anatomy of a Class(Period 1)
Anatomy of a Class
This notebook will explain the structure of a class in Java, including attributes, methods, and instantiation. It will also include examples and a mini-project that requires fixing broken code.
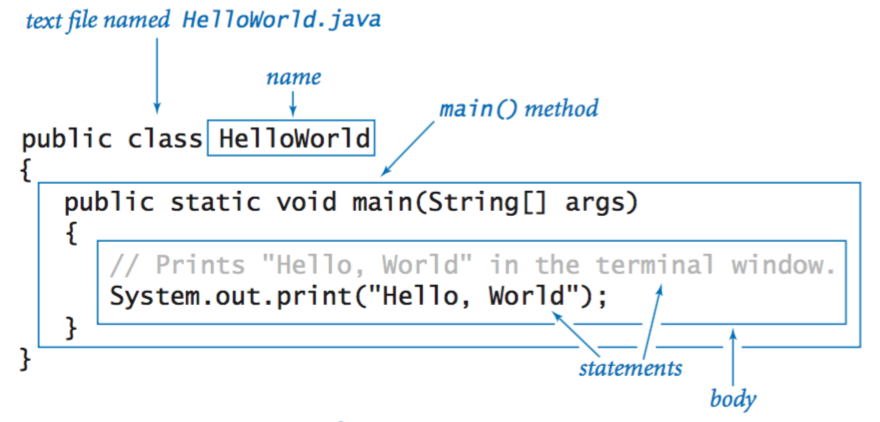
1. Introduction to Classes
- A class in Java is a blueprint for creating objects. It defines a data structure that includes methods and attributes.
- Example:
public class Car {
// Attributes
String model;
int year;
// Method
void drive() {
System.out.println("Driving the car.");
}
}
This Car class has attributes model and year, and a method drive() that prints a message.
2. Attributes and Methods
- Attributes (or fields) are variables that belong to an object.
- Methods are functions that belong to a class.
- Example:
public class Person {
// Attributes
String name;
int age;
// Method
void greet() {
System.out.println("Hello, my name is " + name);
}
}
In this Person class, name and age are attributes, and greet() is a method.
3. Constructor
- Constructors are special methods used to initialize objects.
- They have the same name as the class and do not have a return type.
- Example:
public class Person {
String name;
int age;
// Constructor
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
void greet() {
System.out.println("Hello, my name is " + name);
}
}
This Person class includes a constructor to initialize name and age.
4. Class vs. Instance Variables
- Instance variables are attributes specific to each object.
- Class variables (static variables) are shared among all instances of the class.
- Example:
public static class Car {
// Class variable
static int numberOfCars = 0;
// Instance variables
String model;
int year;
// Constructor
public Car(String model, int year) {
this.model = model;
this.year = year;
numberOfCars++;
}
}
Car mortCar = new Car("MortCar",1995);
System.out.println(mortCar.model);
System.out.println(mortCar.year);
MortCar
1995
Here, numberOfCars is a class variable that keeps track of how many Car objects have been created.
5. Mini Project: Fix the Code
- Below is a class with broken code. The goal is to fix the class so it properly initializes and uses instance variables.
-
Broken code:
- Task: Debug the
Bookclass so it correctly initializestitleandauthor. Consider how the constructor should be modified.
public static class Book {
String title;
String author;
// Fixed Constructor
public Book(String title, String author) {
this.title = title;
this.author = author;
}
}
Book mortBook = new Book("Why You Shouldn't Use Paper","John Mortenson");
System.out.println(mortBook.title);
System.out.println(mortBook.author);
Why You Shouldn't Use Paper
John Mortenson
- Task: Debug the
Bookclass so it correctly initializestitleandauthor. Consider how the constructor should be modified.